KubeRPC is a lightweight kubernetes-native RPC framework designed to enable seamless and low-latency communication between microservices in a Kubernetes cluster.
What exactly is an RPC framework?
Remote Procedure Call(RPC) is a protocol that allows a program to request a service or execute a functionon another program running on a different server as if it were a local function call.
It handles the communication between the two systems, making distributed systems work smoothly.
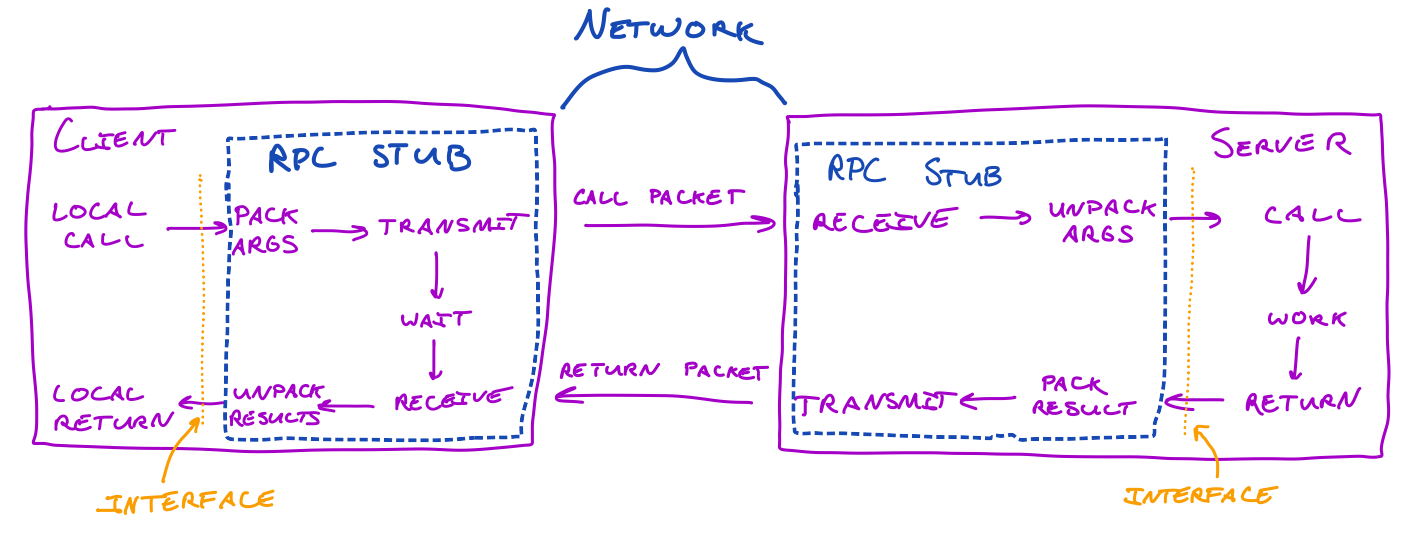
Implementing Remote Procedure Calls, Birrell & Nelson, 1981
Why KubeRPC and why should you care?
One of the main points of controversy when transitioning from a monolithic architecture to a microservice based architecture is the increased latency overhead due to the shift from in-memory function calls to network calls.
Over time, many solutions have been developed to address this challenge, but most are not kubernetes-native and often require complex serialization protocols or additional declarative languages.
These add layers of complexity to the transition process, making it difficult to integrate with existing systems.
Key Features of KubeRPC
- Designed specifically for Kubernetes environments, ensuring seamless integration with minimal overhead.
- Enables straightforward JSON-based service discovery and remote method invocation with retries and timeouts.
- Provides intuitive SDKs for easy integration, reducing setup time and complexity.
- Optimized for scalability, supporting dynamic service registration and adaptable to various microservice architectures.
Under the hood
KubeRPC consists of a core component written in Go, which acts as a service discovery layer and source of truth.
Service Discovery?
The core component watches the cluster and registers available services by leveraging the kubernetes API.
Serialization Protocol?
KubeRPC makes use of the JSON we know and love as the serialization protocol, making it easy to integrate with existing systems and services.
Why JSON though, doesn’t it have performance issues?
While JSON is not the most performant serialization format, especially when compared to binary formats like protobuf, it is widely supported and easy to work with.
KubeRPC combines the best of both worlds. Although JSON is used for communication, the payload is compressed using MessagePack, a more efficient binary serialization format.
This ensures better performance without sacrificing the simplicity and compatibility of JSON.
How does it work then?
When a service is registered, the core component creates a Kubernetes service object with the necessary metadata, including the service name, namespace, and port.
The service object is then used by the client SDK to discover and communicate with the service.
When a client invokes a remote method on a service, the core component looks up the service object and opens a tcp connection to the service pod, sending the commpressed JSON payload over the wire for processing.
What about the SDKs?
The SDKs available allow you to easily interact with the core service, enabling you to register methods and invoke remote methods on other services in an abstracted yet intuitive manner.
Getting Started with KubeRPC
Getting started with KubeRPC is as easy as deploying a Helm chart to your Kubernetes cluster. Just run the following command, and you’re ready to go!
helm install kuberpc-core https://github.com/darksuei/kubeRPC/raw/main/helm_chart/kuberpc-core-0.1.0.tgz --namespace <your-namespace> -f /path/to/custom-values.yaml
Too much talk, show me a demo!
To see KubeRPC in action, you can use the docker compose demonstration, which includes the KubeRPC core, a client, and a server.
This demo showcases how KubeRPC facilitates seamless communication between services as if they were just function calls.
Give it a shot
Ready to simplify your microservices communication? Give KubeRPC a try today!